A popliteal fossa is a shallow hollow within a joint. This hollow is located on the underside of the tibia and can be found on either side of the knee joint (putamen) or between the knee caps (gustavoid). The popliteal fossa contains four main folds, all of which are made up of posterior muscles and ligaments. Superimposed over each of these folds is a narrow groove.
Popliteal grooves are typically seen as indentations in the tissue that surrounds joints and can be found anywhere in the body from the face to the pelvis. The most common of these grooves is the superomedial groove, which is found inside of the popliteal cavity on the tibia and fibula. Superior, inferior, and inferior popliteal grooves can also be found on other structures including the knee, hip, ankle, wrist, and shoulder joint.
The superomedial groove, or superomedial branch, is formed on top of the popliteal cavity on the tibia. Inferior and superior popliteal branches are usually found inside of a groove on the exterior surface of the tibia. A superolateral popliteal branch is found within the superomedial groove.
There are a number of reasons why the popliteal cavity becomes narrowed. It can be caused by injuries to the tendons around the joint, infections in the joint or in the bones surrounding it, the buildup of pressure in the joint, and other factors. The most common cause of this narrowing is the buildup of pressure in the joint, which occurs when there are poor muscle tone and/or weak tendons in the joint.
The popliteal ramus is also known as bony prominences because it forms bumps in the soft tissues of the body that surround the joint. These irregularities can appear as grooves or depressions in the surface of the tissues. These depressions can enlarge and harden if the pressure increases.
Due to the protrusions in the tissue around the popliteal cavity, it is also called the periosteal region and is often referred to as a removed bump. Popliteal cavities tend to repeat at different rates throughout the life of the joint. While most are closed and relatively smooth, others are less smooth and repeat over time. This type of unevenness in the joint can even lead to more permanent dents.
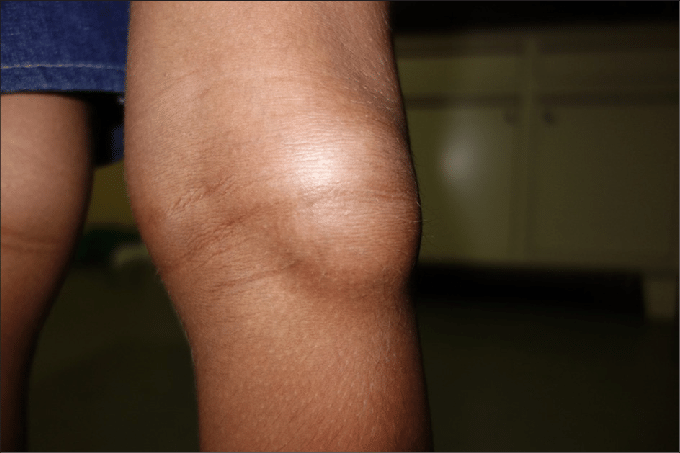
The soft tissue around the bulge is often displaced, which can be uncomfortable and painful. The repetition of this bump can happen suddenly. It may even be asymptomatic, so it's important to take note of this and consult your doctor if you notice this during your routine check-up.
Clicks that can be heard from the popliteal cavities can also be heard as clicks when walking, running, or bending over. This clicking sound can occur even when standing up from a sitting or sitting position.
A popping sound can also be heard when tilting and lifting objects. Mild pain may also be felt when these items are lifted. The clap sound can also be heard when the wrist is turned. However, clapping sounds can also be heard if you bend your knee and try to reach something with both hands or feet. This type of cotton can be caused by the opening of bone protrusions.
Another common cause of the popping sound in the popliteal fossa is the buildup of pressure around the inside of the bone. When the pressure is increased, the bone becomes weak and brittle, which can cause the bump to pop or bulge out. Another reason for this condition is the build up of scar tissue surrounding the bony prominences, which results in a raised bump. Sometimes, this bump can be found to be very noticeable at the back of the ear.
Common causes of this condition include arthritis, an injury to the tendons around the joint, trauma, and infection in the bony prominences. Some studies show that it can also occur from the buildup of plaque on the inside of the bony prominences. People who experience repetitive strain on their joints, such as lifting heavy objects, may also be at risk. If you have symptoms of this condition, it's important to visit a doctor to rule out any serious health issues.
Popliteal bony prominences are not dangerous and require no medical intervention. However, they do require immediate treatment if you're experiencing a popping sound while walking, running, or bending.