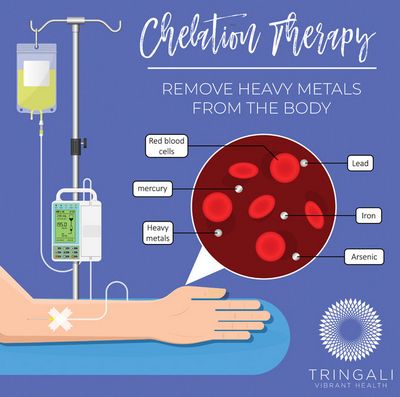
Chelation is a medical process which involves the administration of ionic chelating agents in the body to remove heavy metal deposits. Some of these metals include lead, mercury and aluminum. It has also been found to be effective against other illnesses such as ADHD, cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
Today, there are a variety of chelation therapies available for treating conditions ranging from arthritis to atherosclerosis. The majority of these therapies are administered through intravenous infusions. However, there are also methods of administering them via oral ingestion. This makes use of a variety of supplements that can either be used orally or intravenously.
In many cases of chelation therapy, one will find the need for more than one treatment. For example, if a patient is suffering from a particular condition, more than one treatment may be required. One such case is arthritis. In this particular ailment, several treatments would be necessary before seeing any positive effects. There are a number of ways in which arthritis can be treated by chelation.
Chelation can be accomplished through a process known as chelation inversion. It involves taking a chelating agent which is injected into the site of arthritic activity and leaving it overnight. When the next dose is taken, the first dose will have been completely metabolized and excreted by the body.
Many chelation therapies involve the administration of chelation agents. One of these types of agents is sodium bicarbonate. This is basically the carbonate form of bicarbonate. It can cause severe damage to kidney tubules and kidney tissue, thus leading to the formation of calcium stones. It must, however, be handled with great care so as not to cause further damage to the kidneys or other organs.
Another common chelation agent is potassium bicarbonate. This is commonly used to reduce the toxicity of aluminum and other metals. It is often combined with calcium chloride for this purpose. This mixture is then injected into the arthritic areas where calcium and potassium are needed to neutralize the toxins.
Some chelation therapies also use vitamin D as an active ingredient. These are used to increase calcium retention in the body as well as help detoxify the system. The best way to absorb these vitamin D supplements is by taking them orally. However, for the most part, they are used in conjunction with calcium and bicarbonate chelation therapies. to stimulate the action of an enzyme called glutathione, which is naturally present in the body.
It is important to note that not all patients suffering from heavy metal toxicity need chelation treatments in order to treat their condition. It is also important to note that there is no such thing as a heavy metal toxicity-free patient. As mentioned earlier, everyone is unique and has unique needs.
Types of chelation therapy
There are two types of treatment modalities available for chelation therapy: intravenous and oral. In case of the intravenous therapy, the patient is injected with a high dose of chelating agent. He should also drink plenty of water to keep himself hydrated throughout the procedure.
On the other hand, in case of the oral chelation treatment, the patient is given a solution that is designed to dissolve the deposits in his body through the mouth. He should swallow this solution after each dosage.
There are also many ways in which chelation therapy is administered, as some physicians use injection and others opt for the oral chelation therapy. While the process is done under the care of a physician, a patient is expected to follow any instructions given. As with anything, excessive chelation therapy can have serious consequences, so one must be careful and not overdo it.
The effects of chelation therapy can vary depending on the patient’s condition. Therefore, it is essential that one follows the doctor’s orders closely to avoid any unwanted complications.